Both Industry 4.0 and IoT (internet of things) refer to the changes the manufacturing industry is currently experiencing, however, according to their definitions, the two terms are not interchangeable. Industry 4.0 refers to the fourth wave of the industrial revolution, while IoT refers to the connectivity of devices and the benefits that can bring to consumers as well as business. Here’s a primer on the two technologies.
Both Industry 4.0 and IoT are impacting the manufacturing industry – but they are not the same thing.
Industry 4.0 Definition and History
 Industry 4.0 is a term coined by the German government to define a collective set of technologies that support the digital transformation of manufacturing. At the Hannover Industrial Fair in 2013, the Working Group on Industrie 4.0 presented a paper outlining the four core requirements.
Industry 4.0 is a term coined by the German government to define a collective set of technologies that support the digital transformation of manufacturing. At the Hannover Industrial Fair in 2013, the Working Group on Industrie 4.0 presented a paper outlining the four core requirements.
- Interoperability: The ability of machines, people, sensors, devices to communicate using Internet technology.
- Transparent Information: The ability to use rich digital models representing a physical reality supplemented by data from sensors to create high-value contextual information.
- Technical Assistance: The ability for technical systems to assist human decision making and problem-solving by rapidly aggregating and creating visual representations of data. Secondly, technology systems should assist or replace humans in completing tasks that are dangerous or unpleasant for humans.
- Decentralized Decisions: The ability for technology solutions to make decisions on their own based on rules and to recognize exceptions and special cases and send them to humans for resolution.
Since the 2013 Hannover Fair, the term Industry 4.0 has evolved to mean a collective set of technologies that are transforming manufacturing. These technologies include 3D printing, Internet-connected smart sensors and machines (the Internet of Things), machine learning, artificial intelligence, Nano-technology, Big Data analytics, virtual reality, digital twins, and robotics.
Industry 4.0 definition:
A collective set of technologies that are transforming manufacturing that include the four core requirements (interoperability, transparent information, technical assistance, and decentralized decisions).
A recent McKinsey report lists more than 30 technologies that can fall under the umbrella of Industry 4.0. The common denominator is that they all contribute to the digital transformation of manufacturing in some way.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution
Industry has undergone three major transformations or waves that caused a break with the prior manufacturing models., followed by Industry 4.0 – which we are experiencing right now.
- Steam Engines: The widespread adoption of the steam engine drove the first wave when society moved from a largely agrarian economy to a more industrialized society.
- Electricity: The availability of electricity to drive machinery for mass production ushered in the second wave, which focused on reducing the costs and complexity of manufacturing.
- Computers: Computerized systems like CAD/CAM, ERP and MES made large-scale production more manageable and brought about the third wave.
- Our Current Revolution: Industry 4.0 continues the move to reliance on digital technology, but the technologies are evolving so quickly that they are completely changing manufacturing models. The speed of the transformations and the scope of are causing rapid changes in manufacturing models and even the products companies produce.

Understanding Industry 4.0 and IoT
Some people use the terms IoT and Industry 4.0 interchangeably, but they are not synonymous. IoT is a subset of Industry 4.0, one of the core technologies that support digital transformation.
Industry 4.0 IoT refers to machinery and equipment with attached sensors. These sensors monitor production processes and dispatch information for analysis and reporting.
IoT is simply a subset of Industry 4.0.
Technological Advancement
Machinery and equipment have had sensors connected for many years, but it wasn’t until two additional technologies matured that the true value of connected devices could be achieved. In the past, the sensors might collect data about the process parameters failing, but it might take weeks or months to gather and analyze the data with existing technologies. During that time, the process would continue to create out-of-spec materials, costing a loss of productivity as well as potential scrap.
Now, those sensors may monitor temperature or dimensions in a manufacturing process. These sensors continuously send information about the process to data analysis engines. When the measured parameter approaches a preset threshold, the system sounds an alert notifying humans—or robots—that the process is moving out of control. The rapid notification about the problem enables a quick response, preventing the process from generating large amounts of scrap or rework. This saves money and improves productivity while helping to ensure customer satisfaction.
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
That is the value of IoT, also sometimes called IIoT for Industrial Internet of Things. The true value of connected devices could not be realized until the emergence of several additional technologies: Internet connectivity for fast movement of the data; Big Data analytics engines for rapid analysis; and visualization to make the results easily understood for quick, confident decision-making.
While other industries and consumer applications also rely on IoT technology, its most valuable and transformative use case is in manufacturing.
Other Emerging Industry 4.0 Technologies
Along with Industry 4.0 IoT solutions, it’s the confluent maturation of many technologies that are truly driving the digital transformation.
3D Printing
For example, 3D printing has changed the way manufacturers create prototypes. As printer speeds improve, 3D printing is taking over more and more high-volume manufacturing operations as well as reducing inventory by printing spare parts on demand. Companies that require spare parts for maintenance often stock millions of dollars in parts just in case they ever need them. Sometimes, the same item is stocked in multiple locations to reduce the risk of unplanned downtime. Using 3D printing to create spares on-demand results in massive cost savings and reduces lost productivity.
Robotics
Robotics has changed manufacturing because of the robot’s ability to perform repetitive tasks precisely for long periods. This has saved human workers from boredom and repetitive stress injuries. Robots also undertake dangerous operations or work in hazardous environments that humans can’t tolerate. This capability reduces costs and increases safety while ensuring consistent product quality.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are revolutionizing repetitive tasks and business processes by automatically processing or dispositioning routine transactions or events. When exceptions occur, they refer the case to a human who can resolve the issue quickly. By freeing people from boring mundane tasks, workers can focus on more high-value activities such as creating new products or providing exceptional customer service.
Nano-Technology
Nano-technology is also revolutionizing manufacturing. Nano-bots are tiny machines which can be used to create other machines. This enables rapid creation of new products with a high degree of precision.
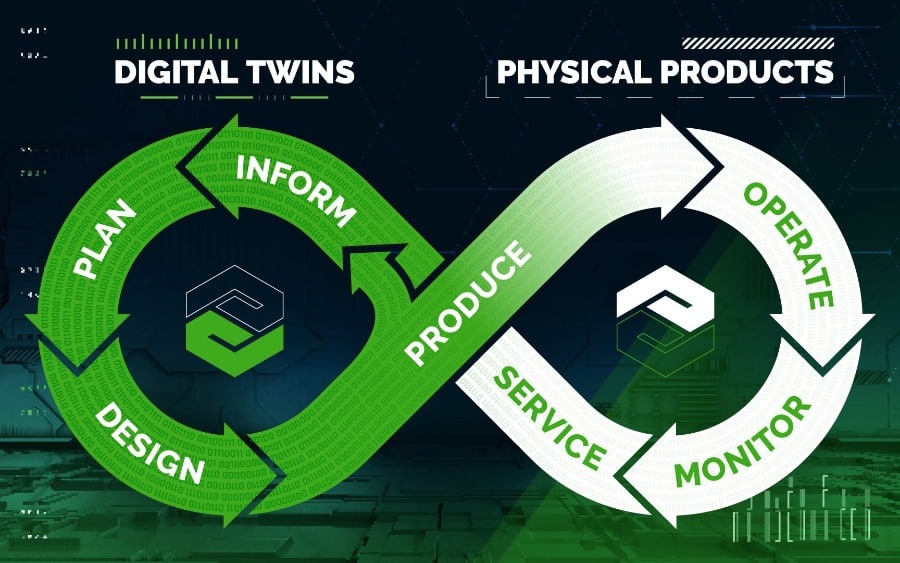
Digital Twin
Digital twinning is the creation of a digital model of a real-world product process. By creating a digital twin, engineers can review the entire production process virtually and eliminate waste or non-valued-added steps. They can easily evaluate where tools or jigs would improve a process by eliminating errors that can lead to poor quality.
Virtual reality allows engineers to watch customers interact with their design without having to create expensive physical prototypes. This helps them make design decisions quickly and brings products to market faster.

Where Do We Go from Here?
These are just a few of the technologies that make up Industry 4.0. It’s easy to see that the collective technologies are truly ushering in a new wave of manufacturing. In order to fully take advantage of the newest manufacturing technologies, it is essential that organizations have advanced platforms and tools to support their needs. At 3HTi, we offer a range of solutions to support manufacturing. If you are interested in learning more about our available services and technology, contact us.