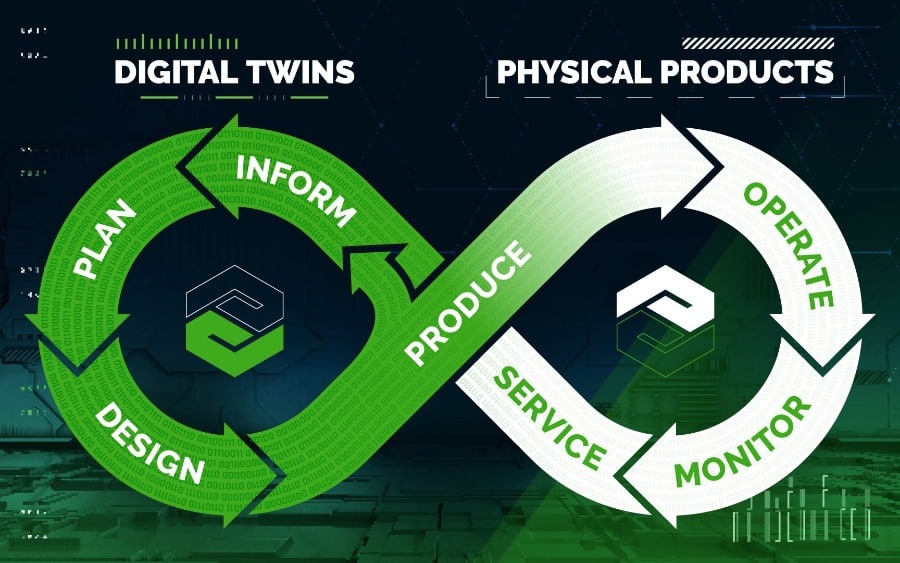
Discrete manufacturing industries have quickly and readily adopted Industrial IoT applications, greatly expanding the use cases and the solution environment. As a result, companies now place a greater emphasis on seamless integrations, diverse technology portfolios, and domain expertise to ensure the continued success of projects.
A recent PTC survey found that 89% of respondents expect to transition their industrial IoT applications to production environments within a year or less. As a result, these organizations are leveraging more pre-built solutions and looking to utilize technology from companies with brand portfolios and multiple technology and implementation partners.
As the push for connected operations continues to grow, organizations are utilizing pre-built technology solutions to streamline implementation.
The Benefits of Industrial IoT Applications
In every industry, especially manufacturing, companies hope to use their industrial IoT applications to optimize operations. They hope to achieve strategic product differentiation while improving operational productivity and efficiency. They also want to use IIoT applications to address challenges such as continual downward cost pressures and the looming skills gap.
Companies are finding uses for industrial IoT applications in their own factories and in the factories of their end-users. Traditional “Black-box” products such as MRI machines, power transformers, transit systems, material handling and warehousing systems, and other systems are prime targets for industrial IoT applications. They can utilize the use of digital twins to improve predictive analytics and reduce unnecessary maintenance and unplanned downtime.

Manufacturers increasingly rely on IIoT applications, advanced analytics, and augmented reality to improve productivity and throughput in their factories and to improve customer satisfaction by implementing these tools in products used in the field. PTC reports that 38% of its customers’ connected things are remote, showing that maintaining uptime, reducing unnecessary service calls, and improving first-time fix rates are increasingly becoming part of a product’s expected feature set.
The Need for Context
However, to be effective, the use of industrial IoT applications in manufacturing requires seamless connectivity into both new and existing equipment, PLCs, sensors, and other machinery and devices. Beyond seamless connectivity, gaining value from IoT applications requires an IIoT platform to manage and contextualize the data to provide actionable insights.
IIoT applications and connectivity needs to be implemented in new and existing operations.
The most common industrial IoT application use case is still operational intelligence for manufacturing. Operational intelligence accounts for more than 30% of current use cases that target operational effectiveness.
 Predictive maintenance, at 12% of current projects, is driving the shift from reactive to proactive or preventive systems. Analyzing the data from IoT devices with machine learning algorithms and operational thresholds can alert personnel to upcoming anomalies before an interruption occurs. Such early intervention has enormous value in reducing risk and preventing supply chain interruptions.
Predictive maintenance, at 12% of current projects, is driving the shift from reactive to proactive or preventive systems. Analyzing the data from IoT devices with machine learning algorithms and operational thresholds can alert personnel to upcoming anomalies before an interruption occurs. Such early intervention has enormous value in reducing risk and preventing supply chain interruptions.
Projects Address Multiple Areas
Unplanned downtime is extremely expensive and has a ripple effect through the supply chain, affecting costs, logistical planning, and ultimately customer satisfaction. Integration with supply chain and logistical partners as well as customers can minimize the effect by providing an early warning of potential problems, enabling partners and customers to introduce alternate plans that preserve productivity and reduce costs. Remote monitoring and remote service together add up to 12% of existing projects.
IIoT adoption is a global phenomenon, with adoption currently at 35% in the Americas, 30% in EMEA, and 30% in APAC. The entire market is poised for growth, with forecasts reaching more than $1 trillion in the next three to four years.
The IIoT market is expected to grow to more than $1 trillion over the next 3-4 years.
The scope of influence in IIoT projects has expanded beyond manufacturing. While manufacturing still accounts for 46% of the beneficiaries, operations accounts for 19%, and service for 22%. The expansion of roles that can benefit from industrial IoT applications has given rise to a need for more role-based solutions and holistic IIoT solutions that address multiple pain points and present actionable insights to multiple constituents or roles.
Deployment: Pace and Other Considerations
The pace of deployment continues to speed up, with 89% of customers expected to move their current projects into production in the next year.
Companies undertaking an industrial IoT project should give careful consideration to the deployment model and data storage decisions they must make.
 As projects move outside of a factory’s premise to address monitoring equipment at customer sites, on-premise or even wholly private cloud solutions may not provide optimum results. Customers should evaluate their entire technology stack and partner ecosystems at the start of the project and periodically as projects progress and increase in scope because of the rapid advances in technology and the proliferation of industrial IoT applications. For example, the ability to support edge computing is becoming increasingly critical as the amount, variety and value of data increases. Bandwidth and response time are critical components of a successful system, and integration to onsite data management and business solutions such as ERP and CRM is required.
As projects move outside of a factory’s premise to address monitoring equipment at customer sites, on-premise or even wholly private cloud solutions may not provide optimum results. Customers should evaluate their entire technology stack and partner ecosystems at the start of the project and periodically as projects progress and increase in scope because of the rapid advances in technology and the proliferation of industrial IoT applications. For example, the ability to support edge computing is becoming increasingly critical as the amount, variety and value of data increases. Bandwidth and response time are critical components of a successful system, and integration to onsite data management and business solutions such as ERP and CRM is required.
The cloud is a pivotal technology for IoT solutions, and companies should ensure that their technology choices are cloud-native to take advantage of the scalability and massive storage capabilities. Only technologies that can integrate with the entire operational stack for operations will ultimately thrive in the future.
Finding Value in Industrial IoT Applications
Proof-of-value for IIoT projects is becoming evident more rapidly, helping to accelerate the movement to production. It is imperative that the underlying technology streamlines integrations and ensures application maintenance simplicity. No two installations are alike, so companies increasingly turn to pre-built applications that can be easily customized. This is another reason to evaluate the technology’s flexibility and the entire ecosystem including support and partners. Many analysts report that the ideal solution consists of about 80% pre-packaged and coded applications with the remaining 20% available for customization.
As companies undergo their digital transformations, industrial IoT applications will only increase in importance. Executing on an IIoT strategy is an invaluable differentiator, but companies need to select partners with the right mix of technology, domain expertise and partner ecosystem to ensure success. To learn more about the state of industrial IoT applications, contact 3HTi for an IoT consultation today.